+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051



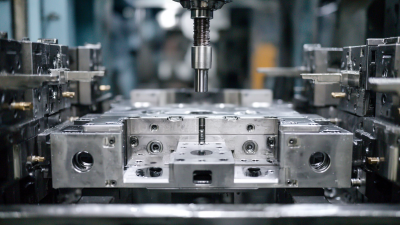
Choosing the right manufacturing process is crucial. Die casting parts offer a variety of benefits. These components are molded under pressure, resulting in precise dimensions. This accuracy is vital for many industries.
Die casting parts use metals like aluminum and zinc. These materials provide strength and durability. They are lightweight yet robust. This combination is appealing for automotive and electronics sectors.
However, the initial cost can be high. Not all manufacturers can invest upfront. It’s important to consider the long-term advantages. Quality and efficiency may justify the expense. Overall, understanding die casting parts is essential for effective decision-making.
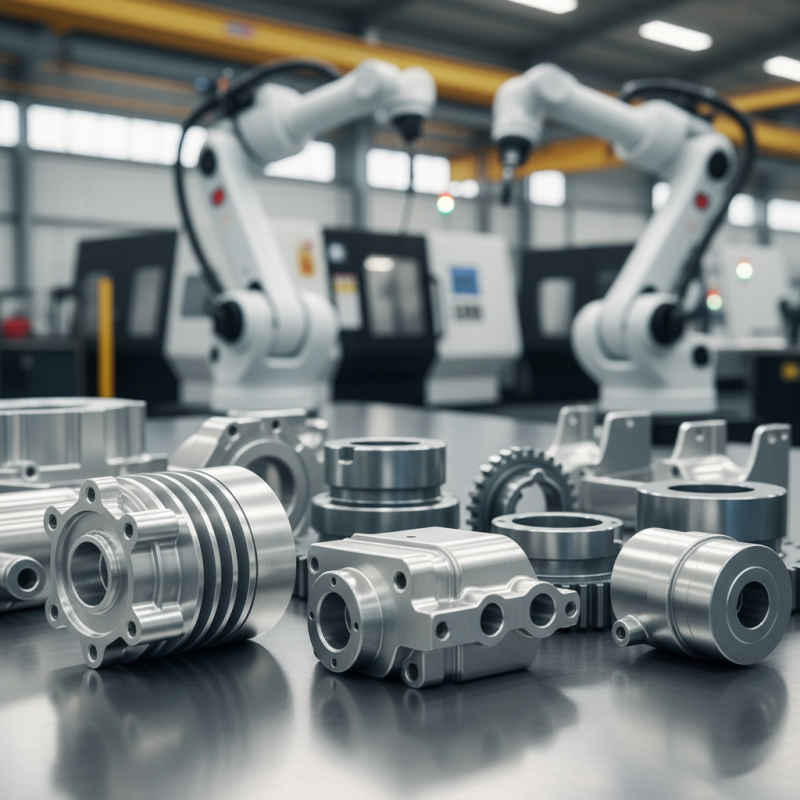

Die casting is a popular choice for manufacturing due to its unique benefits. It allows for the production of complex shapes with high precision. This method also offers excellent surface finishes. As a result, fewer post-production processes are needed.
One key advantage is its efficiency in mass production. Die casting can produce large quantities quickly. This leads to reduced labor costs and shorter lead times. However, the initial setup costs can be high. Manufacturers should weigh upfront expenses against long-term savings.
Tips for optimizing die casting include: carefully designing parts for manufacturability. Complex shapes can increase costs. Use appropriate materials that fit the die casting process. This helps reduce defects and ensures product longevity. Don't overlook the importance of quality control. Regular checks can prevent costly errors.
| Advantage | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High Precision | Die casting allows for tight tolerances, resulting in precise parts that require minimal machining. | Automotive parts, electronic housings. |
| Complex Shapes | The process enables the creation of intricate geometries, which are difficult to achieve with other methods. | Consumer electronics, machinery components. |
| Cost-effective for Large Volumes | Ideal for mass production where the initial setup cost is offset by lower per-part costs. | Mass-produced items, appliance parts. |
| Material Versatility | Compatible with various metals, including aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. | Aerospace components, automotive parts. |
| Improved Surface Finish | The die casting process often yields a better surface finish, reducing overall finishing time. | Decorative items, consumer goods. |
Die casting is emerging as a go-to method for manufacturing parts due to its cost efficiency. A recent report from the Aluminum Association highlighted that die casting can reduce production costs by up to 30% compared to traditional machining methods. This significant saving stems from the ability to produce complex shapes in a single step, minimizing waste and labor costs. Moreover, die cast parts exhibit excellent dimensional stability, leading to fewer defects.
When evaluating production techniques, consider the long-term benefits of die casting. Though the initial tooling costs may be higher, the cost per unit decreases significantly with higher volumes. Studies indicate that companies can achieve a cost per unit reduction of over 50% when committing to larger production runs. Shorter lead times are an added perk that enhances the overall profitability.
Tip: Always analyze your production needs before investing in tooling. Ensure you can meet the quantity needed to benefit from die casting’s efficiencies.
Despite its advantages, die casting is not suitable for every application. Parts with intricate designs or low production volumes may be better suited for alternative methods. Manufacturers should weigh the pros and cons carefully.
Tip: Consult with engineers to determine if die casting aligns with your product design. A detailed feasibility study can save costs in the long run.
Die casting is a popular choice in manufacturing, thanks to its superior material properties and production efficiency. Commonly used materials include aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. Aluminum alloys account for about 60% of the die casting market, with high strength and lightweight characteristics. These properties make aluminum ideal for automotive and aerospace applications. Reports indicate that aluminum die castings can reduce vehicle weight by up to 30%.
Zinc die casting is another prevalent option. It offers excellent corrosion resistance and good strength at elevated temperatures. Especially in industries requiring intricate shapes, zinc parts can be produced with high precision. The material's low melting point allows for quicker cycle times, which enhances overall productivity. Studies have shown, however, that zinc can suffer from brittleness under heavy loads. This raises concerns for manufacturers in high-stress applications.
Magnesium is the lightest structural metal, making it highly desirable. It provides a favorable strength-to-weight ratio, making it suitable for aerospace components. Yet, working with magnesium requires specific techniques. It is prone to oxidation and may not be as durable as other metals. This uncertainty can complicate decision-making for designers. Each material has its pros and cons. Understanding these nuances is crucial for effective material selection in die casting.
Die casting is a versatile manufacturing process. It is used across various industries, especially in automotive and aerospace. These sectors rely on die casting for its precision and strength. Components like engine blocks, transmission cases, and housing parts are often produced using this method.
In the electronics industry, die casting provides enclosures for sensitive components. Its ability to create complex shapes with fine details is invaluable. Companies often face challenges with thermal conductivity and weight. Choosing the right alloy in the die casting process can address these issues effectively.
Tip: Always evaluate the specific needs of your project. Not every part needs to be die-cast. Sometimes, alternative methods might work better.
In consumer products, die casting delivers various lightweight and durable items. Toys, tools, and appliances often benefit from this process. However, it requires careful planning to avoid defects. Small errors can lead to significant production delays.
Tip: Perform a thorough design review before proceeding. It's easier to fix issues in the design phase than on the production floor.

Die casting parts are preferred for their unmatched quality and precision. The process involves forcing molten metal into a mold. This method creates parts with tight tolerances. Each piece is highly consistent and reproduces well.
The intricate details achieved in die casting are impressive. Features like thin walls and complex shapes become feasible. The surface finish is often smooth, requiring minimal post-processing. This saves time and improves overall efficiency in production.
Tip: When selecting die casting for a project, consider the materials used carefully. Different metals can affect durability and cost. Assess your requirements for strength and aesthetic appeal.
Despite the advantages, there are challenges in die casting. High initial costs for molds can be a barrier. It requires a significant investment before mass production begins. This should not be overlooked when planning a project.
Tip: Always evaluate the long-term benefits versus the upfront costs. Analyzing production volume helps justify the expense. A well-considered decision leads to better resource allocation.