+86-13516964051
+86-13516964051



Zinc casting has gained significant attention in the metalworking industry. According to a recent market report, the global zinc die-casting market is projected to reach $5.6 billion by 2027. This growth highlights the increasing demand for zinc due to its excellent properties. Zinc casting offers strength, durability, and resistance to corrosion. Many industries, including automotive and electronics, depend on these characteristics.
Furthermore, the versatility of zinc casting processes leads to its wide applications. Techniques such as hot chamber and cold chamber die casting are popular. Each method has distinct advantages, affecting the final product's quality. However, the industry faces challenges, such as the rising cost of raw materials. These issues push us to rethink our approach to zinc casting.
Despite its benefits, not all zinc casting techniques yield optimal results. Variability in alloy compositions can affect performance. Industry players must continually explore innovations to improve casting efficiency and product quality. This ongoing quest for excellence defines the future of zinc casting. Embracing these advancements can help the industry thrive amid challenges.
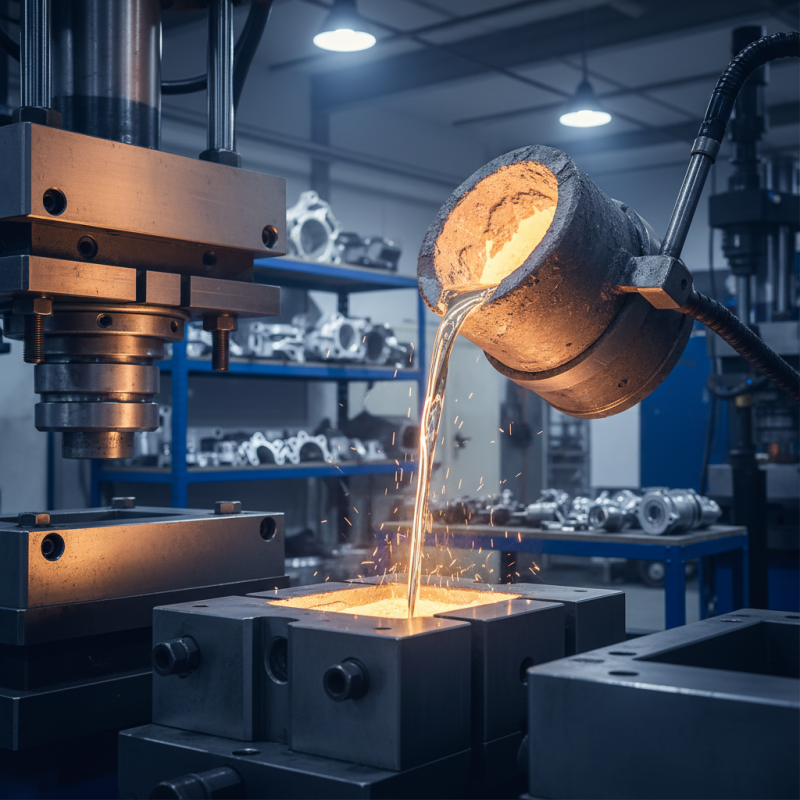

Zinc casting is a key method in metalworking. It offers versatile applications and a variety of techniques. The most common method is die casting. This technique provides high precision and smooth surfaces. However, preparing dies can be expensive and time-consuming. This might limit smaller projects from using it.
Investment casting is another option. It allows complex shapes and features. Yet, sometimes it can lead to inconsistencies in finish quality. Some practitioners find the process tricky, requiring experience to master. Sand casting is also popular, particularly for larger parts. It is cost-effective and suitable for low production runs. Nevertheless, sand casting can result in rougher surfaces.
Centrifugal casting presents unique advantages too. It is useful for creating cylindrical parts. But it requires careful balancing to avoid defects. Overall, while these techniques are effective, they come with their challenges. Each method serves different needs, showcasing the complexity of zinc casting in metalworking. The choice often depends on the project's specific requirements.
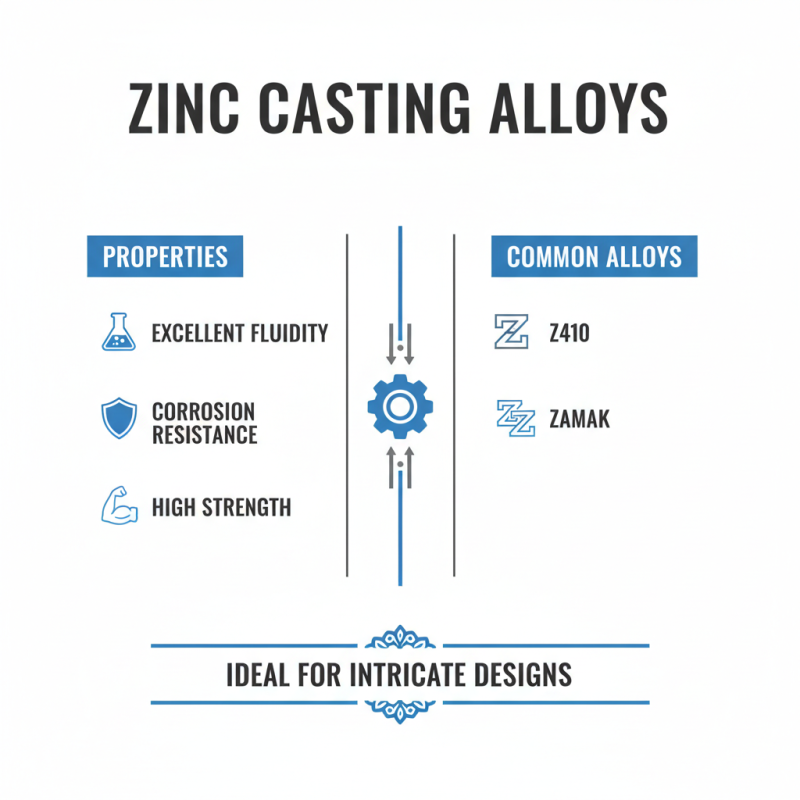
Zinc casting alloys are widely used in metalworking due to their unique properties. Common alloys like Z410 and Zamak provide excellent fluidity during casting. Zamak, for instance, is known for its good corrosion resistance and strength. People often choose this alloy for intricate designs, as it fills molds well.
However, there are challenges in using zinc alloys. Sometimes, issues like porosity can arise. This may affect the final product's quality. It's crucial to carefully control casting conditions. Temperature and cooling rates play significant roles. Improper settings can lead to defects that are hard to fix.
Zinc alloys also show varying hardness levels. For example, Z410 is relatively harder compared to Zamak. This hardness makes it suitable for machinery parts. But, it might not be ideal for delicate applications. Users should consider the end-use carefully. Choosing the right alloy requires a good understanding of its properties.
Zinc die casting is a widely used technique in metalworking. It offers several advantages, such as precision, durability, and the ability to produce complex shapes. The standard method involves melting zinc alloy, injecting it into a mold, and allowing it to cool. This method is efficient and provides high-quality results.
One common application of zinc die casting is in the automotive industry. Zinc parts are lightweight yet strong, making them ideal for vehicle components. They can withstand high temperatures and harsh environments. However, not all designs are feasible. Some intricate shapes may lead to weaknesses or require significant adjustments in the molds.
Another application is in electronics. Zinc casings protect sensitive components from damage. They also provide electromagnetic interference shielding. However, the process must be closely monitored. Inconsistent quality can lead to failures in performance. Overall, while zinc die casting is effective, careful consideration of design and technique is crucial for optimal results.
| Casting Technique | Applications | Advantages | Typical Materials |
|---|---|---|---|
| High Pressure Die Casting | Automotive parts, Electronics enclosures | High precision, Excellent surface finish | Zinc-Aluminum alloys, Pure zinc |
| Gravity Die Casting | Industrial machinery, Construction components | Cost-effective, Good mechanical properties | Zinc alloys, Brass |
| Centrifugal Casting | Pipes, Cylinders | Uniform density, Minimal porosity | High-strength zinc alloys |
| Zinc Sand Casting | Art and decorative pieces, Custom prototypes | Flexible design, Low tooling costs | Zinc, Zinc-Aluminum alloys |
| Lost Wax Casting | Jewelry, Artistic sculptures | High detail, Complex shapes | Pure zinc, Zinc alloys |
Zinc casting has evolved significantly, with innovative techniques enhancing quality and efficiency. Recent industry reports indicate that the global zinc die-casting market is projected to reach $10 billion by 2026. This growth underscores the importance of adopting advanced methods to improve production outcomes.
One promising technique is the use of vacuum-assisted die-casting. This approach minimizes gas entrapment, reducing defects in final products. The result? Higher strength components with improved surface finishes. Data shows that manufacturers can decrease scrap rates by up to 20% when integrating this technique. Still, challenges remain. Not all facilities have the equipment for vacuum processes, which can limit widespread adoption.
Another technique gaining attention is alloy optimization. By refining zinc alloys, manufacturers achieve better fluidity and mechanical properties. Studies suggest that specific alloy compositions can enhance tensile strength by over 30%. However, fine-tuning these blends can be complex, often requiring extensive testing and adjustments. This iterative process can lead to delays, illustrating the balance between innovation and practical execution in zinc casting.
Zinc casting processes face several challenges. One major issue is contamination. Impurities can affect the mechanical properties of the final product. Proper cleaning is essential. Use appropriate tools to avoid introducing foreign materials.
Temperature control is another hurdle. Zinc has a low melting point. If the temperature fluctuates, it can lead to defects like porosity. Consistent monitoring is crucial. Ensure your furnace settings are precise to maintain quality.
Tips: Always perform regular equipment checks. Look for signs of wear and tear. This practice can reduce unexpected failures. Experiment with different zinc alloys. You might discover superior results for specific applications. Reflect on your experiences to improve future casting techniques.